Building Blocks
Building Blocks#
A FAIR Data point consists of many different elements, which in essence are a layer around a traditional database.
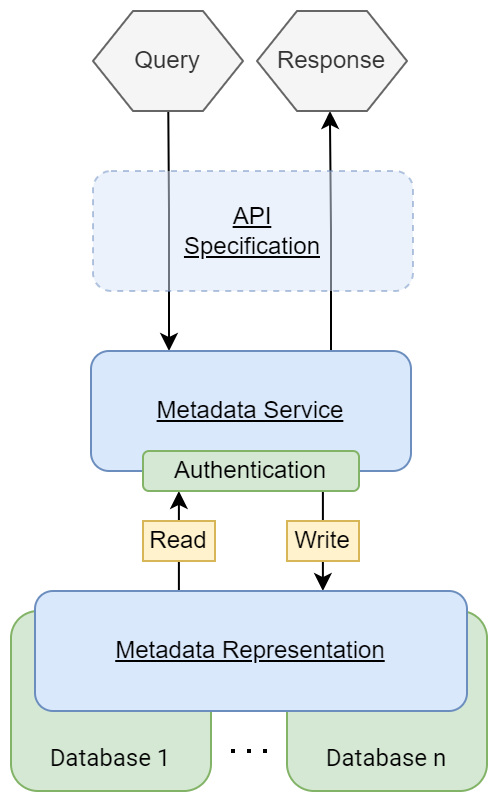
The first component, and most important one, is a definition of the FAIR Data Point “API” specification. It is completely based on semantic metadata standards (mostly Data Catalog (DCAT) and Dublin Core, combined with the Linked Data Platform (LDP)), and based on the REST (Representational state transfer protocol) philosophy.
This combination targets the the highest possible technical interoperability in combination with a relatively simple implementation. The FAIR data point protocol comes with a tool that can be used to test the compliance of an implementation.
The second component is a reference implementation of the metadata registration service: A service implementing the API specification. It contains an authentication system to allow maintainers to define and update metadata. Read-only access to the data is public. It includes FAIR Accessor and Security Enforcer architecture blocks.
The third component includes a Metadata representation with the automated possibility to browse on metadata and request actual data through this metadata layer. All the operations on metadata, actual data, requests and responses is logged in the Metrics Gatherer. It can also contain some metrics on how often specific organizations request data, and which data is being requested very frequently.
